Introduction Fire safety is more than just having fire extinguishers and alarms — it’s about building resilience into structures and systems. Passive fire protection methods are an essential part of any fire safety strategy, designed to contain and slow the spread of fire, giving occupants more time to evacuate and minimizing property damage. Understanding these methods is key for any business or building owner committed to comprehensive fire protection. What is Passive Fire Protection? Passive fire protection (PFP) refers to building construction features and systems that help contain a fire and limit its spread without human intervention. Unlike active fire protection — such as sprinklers or alarms — PFP works quietly and continuously as part of a building’s design. Examples of passive fire protection include: Fire-resistant walls and floors Fire doors Firestopping materials Fire-resistant coatings These systems are vital in ensuring both structural integrity and the safety of occupants. Common Passive Fire Protection Methods Fire-Resistant Building Materials Materials like gypsum boards, concrete, and fire-rated glass are designed to withstand heat and slow fire spread. Tip: Ensure materials meet local fire safety regulations and are certified for fire protection. Fire Doors and Compartmentation Fire doors prevent fire and smoke from moving between compartments, allowing safe evacuation routes. Compartmentation divides a building into sections to contain fire and smoke. Tip: Regularly inspect fire doors and ensure they close automatically without obstruction. Firestopping Firestopping involves sealing openings in walls, floors, and ceilings with fire-resistant materials. Tip: Hire certified fire protection professionals to perform firestopping work to meet fire safety codes. Benefits of Passive Fire Protection Enhanced Safety: Gives occupants more time to evacuate safely. Reduced Property Damage: Slows fire spread, protecting valuable assets. Compliance: Meets fire safety regulations and building codes. Long-Term Cost Savings: Reduces losses and insurance claims due to fire damage. Conclusion & Call-to-Action Passive fire protection is a cornerstone of effective fire safety and fire protection strategies. By integrating PFP measures into building design and maintenance, you can protect lives, property, and your business reputation. 💡 Ready to strengthen your building’s fire safety? Visit Safety Source Limited or contact us today for expert advice on the best passive fire protection methods for your property.
Understanding Fire Protection: Essential for Every Home and Business
Fire protection isn’t just a safety requirement — it’s a vital investment in life and property. Every year, fires cause devastating losses in homes and businesses worldwide, making prevention a priority for every responsible owner. Whether you run a small shop or manage a large facility, having a robust fire protection system is a necessity, not an option. In this article, we’ll explore why fire protection matters, the types of systems available, and practical steps you can take to ensure safety. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to safeguarding your property and loved ones. What is Fire Protection and Why It Matters Fire protection refers to a set of measures designed to prevent fire incidents, control their spread, and ensure safe evacuation. It includes equipment such as fire extinguishers, alarms, suppression systems, and fire safety training. The importance of fire protection is clear: fires can start anywhere, often without warning. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), U.S. fire departments responded to nearly 1.3 million fires in 2023, causing over $14 billion in property damage. The costs extend beyond physical loss — lives, reputation, and business continuity are also at stake. Real-Life Example:In 2019, a commercial warehouse in London suffered a major fire that destroyed goods worth millions. The lack of proper fire protection equipment and an outdated alarm system delayed evacuation, resulting in greater losses. This incident highlights why every building must have a robust fire protection plan. Key Elements of Fire Protection 1. Fire Prevention Prevention starts with awareness. Fire hazards can come from electrical faults, flammable materials, or human negligence. Regular inspections and maintenance help mitigate these risks. Best Practices: Conduct regular safety audits. Ensure electrical wiring meets safety standards. Store flammable materials properly. 2. Fire Detection Early detection saves lives. Fire alarm systems, smoke detectors, and heat sensors detect anomalies and trigger alerts. Modern systems can even send alerts directly to smartphones or fire departments. Example:A restaurant in New York City recently avoided a potential disaster because a heat sensor detected an electrical fault in the kitchen early enough for staff to evacuate and call emergency services. 3. Fire Suppression Suppression systems limit the spread of fire. Sprinklers, foam systems, and CO₂ suppression systems are common solutions, depending on the facility type. Choosing the right system is crucial to minimize damage. 4. Safe Evacuation Evacuation plans and proper signage are essential. Emergency lighting and marked escape routes guide occupants to safety in smoke-filled conditions. Regular fire drills make evacuation smooth and effective. Why Fire Protection is a Strategic Investment Fire protection isn’t merely a regulatory requirement — it’s a strategic safeguard. Businesses that invest in robust safety measures enjoy: Reduced insurance premiums. Lower risk of catastrophic losses. Improved employee and customer confidence. A case study of a manufacturing plant in Germany showed that investing in advanced fire suppression systems reduced downtime and saved the company $1.2 million in potential damages over five years. Practical Steps to Implement Fire Protection Step 1: Conduct a Fire Risk Assessment Identify hazards, assess risks, and plan preventive measures. Many fire safety consultants offer professional assessments tailored to specific facilities. Step 2: Install Appropriate Fire Protection Systems Choose systems that fit your property type. Residential units might rely on smoke alarms and extinguishers, while industrial facilities may need sprinklers and advanced suppression systems. Step 3: Train Staff and Residents A well-trained team is your first line of defense. Regular fire drills and training sessions ensure everyone knows their role during emergencies. Step 4: Maintain Equipment Regularly Fire protection systems work only when they are maintained. Schedule regular inspections, replace faulty equipment, and upgrade outdated systems. Conclusion Fire protection is a responsibility every home and business owner must embrace. It goes beyond compliance — it’s about protecting lives, property, and livelihoods. A well-planned fire safety strategy integrates prevention, detection, suppression, and evacuation. Investing in fire protection today means preventing disasters tomorrow. Don’t wait for a fire to teach you the importance of safety — act now. Call to Action:If you’re ready to strengthen your fire protection plan, contact our safety experts today. We provide tailored solutions to protect your property and peace of mind.
Comprehensive Guide to Fire Safety Systems, Equipment & Services in Bangladesh
Introduction Bangladesh has witnessed a series of devastating fire incidents in recent years. According to the Bangladesh Fire Service and Civil Defence (FSCD), there were 26,659 fire incidents in 2024, causing 140 deaths and injuries to 341 people. The financial loss was estimated at Tk 447 crore, while proactive firefighting saved assets worth over Tk 1,974 crore. Shopping malls, factories, and high-rise commercial buildings remain at the highest risk due to poor compliance with the Bangladesh National Building Code (BNBC) and lack of active fire protection systems. In this context, Safety Source Ltd. provides end-to-end fire safety, electrical safety, and digital solutions to ensure compliance, safety, and business continuity. 🔥 Fire Protection Systems in Bangladesh Fire Fighting Pump Systems Reliable pumps are the backbone of any fire suppression system. Safety Source Ltd. supplies: Horizontal Split Case Fire Pumps (Diesel & Electric) End Suction Fire Pumps Vertical Turbine Fire Pumps Each system is equipped with controllers, jockey pumps, motors, and accessories to ensure uninterrupted firefighting capacity — vital in Dhaka’s congested commercial zones where municipal water supply may fail during emergencies. Valves & Accessories Valves ensure system reliability and safety. Our product range includes: OS & Y Gate Valves Butterfly Valves, NRVs, Alarm Valves Landing Valves, Breaching Inlets Flow & Pressure Switches MS Pipe & Fittings Durable piping systems are essential for fire hydrant networks. We supply: MS Pipes (Schedule 40) Grooved, Welded & Threaded Fittings Flanges and Accessories Sprinkler Systems Sprinklers remain one of the most effective tools in stopping a fire at its source. We provide: Upright, Pendent, Sidewall & Concealed Sprinklers Quick Response & K-Factor Sprinklers Foam & Gas Suppression Systems For high-value facilities like data centers, garment factories, and banks, we provide: Foam, Wet Chemical & Powder Systems Clean Agent Systems: FM-200, NOVEC 1230, Inert Gas 🚨 Fire Detection Systems Early detection saves lives. Bangladesh has seen fires in high-rise buildings where alarms were absent or non-functional. Safety Source Ltd. installs systems from TRIGA, COOPER, SHIELD, Simplex, and Maple Armor including: Smoke, Heat & Multi-Sensor Detectors Addressable Control Panels Beam & Duct Detectors Manual Call Points, Sounders & Relays 🚪 Fire Doors In Bangladesh, lack of fire doors has turned many fires deadly by allowing smoke to spread unchecked. We supply fire-rated doors from: NAFFCO – Steel, Acoustic & Glazed Doors ASICO – Fire Resistant & Glazed Doors 🛡️ Passive Fire Protection Fire Retardant Paints (Cementitious & Intumescent) Fire Smoke Curtains These systems delay fire spread, giving occupants crucial escape time. 🧯 Fire Safety Equipment Fire Extinguishers (ABCE, CO₂, Foam), Auto Fire Ball Exit Signs, Emergency Lights, Fire Blankets & Buckets Safety Gear (Helmets, Gloves, Fire Suits, Boots) Rescue Equipment (Stretchers, Ropes, Axes, Ladders, Ventilation Fans) ⚡ Electrical Safety Solutions Electrical faults remain a leading cause of fires in Bangladesh. Safety Source Ltd. provides: Bus Bar Trunking Systems (Lighting, Plug-in, Power) Lightning Protection Systems Circuit Protection (MCB, MCCB, ACB, VCB, Load Break Switch) 🎨 Digital Media & Printing We also support corporate branding needs: Printing (PVC, Vinyl, 3D, UV, Reflective) LED Signs, Neon Signs, SS Letters, Laser Engraving Custom Branding (ID Cards, Pens, Crests, Rubber Stamps) Large Format: Billboards, Banners, AutoCAD & Blueprint Prints 🛠️ Services Beyond products, Safety Source Ltd. provides: Consultancy: Fire system design, evacuation planning Installation: Fire alarms, sprinklers, hydrants, extinguishers, fire doors Inspection & Maintenance: Pumps, detection, PA systems, emergency lights Extinguisher Refilling & Customized Plans Electrical & Structural Safety Audits ✅ Why Choose Safety Source Ltd.? Complete Solutions: Fire safety + electrical + branding under one roof Trusted Brands: International standards, BNBC-compliant systems Industry Expertise: Garments, data centers, offices, shopping malls, factories Ongoing Support: From design to maintenance 📊 Bangladesh Fire Safety Scenario: Why This Matters Fires like the Green Cozy Cottage Mall fire in Dhaka (2024) killed over 40 people, mainly due to lack of hydrants, fire doors, and sprinklers. FR Tower Banani fire (2019) killed 26 and exposed poor compliance with BNBC. FSCD statistics show malls and factories are among the most vulnerable. This proves that proper fire protection systems are not optional — they are life-saving essentials. ✅ Why Choose Safety Source Ltd.? • Complete Solutions: From fire safety to branding — all under one roof • Trusted Brands: International standards and certified systems • Industry Expertise: Solutions for garments, data centers, factories, offices • Ongoing Support: From design to maintenance, we’re with you every step
Why every shopping mall in Bangladesh must install fire hydrants
Shopping malls are meant to be places of leisure, commerce and safety — but the tragic pattern of recent fires in Bangladesh shows they can quickly turn into deathtraps when active fire-fighting measures and building safeguards are missing. Installing properly designed and maintained fire hydrant systems in every mall is not a luxury: it’s a practical, evidence-based lifesaver that protects people, property and the city’s emergency response capability. Below I lay out the real data, local scenarios, building-code context, and practical recommendations for Bangladesh — with sources you can check. The scale of the problem (real data from Bangladesh) Bangladesh recorded 26,659 fire incidents in 2024, with 140 deaths and 341 injured, according to the Fire Service & Civil Defence (FSCD) press release summarized by national outlets. That’s roughly 73 fires per day. These incidents caused estimated property damage of TK 447 crore while the FSCD reported saving TK 1,974 crore in value from fires. The Business Standard Mall and high-rise building fires have produced some of the most deadly single incidents. A severe blaze at the six-storey Green Cozy Cottage shopping mall (Dhaka) in March 2024 killed dozens (reports put the toll at 43–46 dead) and exposed problems such as unauthorized use of spaces, blocked or absent emergency exits, and inadequate fire protection measures. Survivors were evacuated to roofs and rescued by firefighters. Al Jazeera+1 Earlier high-rise disasters (e.g., the FR Tower fire in Banani, Dhaka, 2019) demonstrated similar failures: lack of sprinklers, insufficient fire exits and rapid smoke spread that trapped occupants. Those events underscore that multi-storey commercial buildings need reliable, internal firefighting infrastructure. Wikipedia+1 What is a fire hydrant system and why it matters for malls A fire hydrant system for a building typically means an internal wet or dry standpipe network, hose reels/hose connections on each level, adequate water storage (or connection to a reliable external water main), fire pumps (with backup power), and external street-side hydrant points where needed. It gives firefighters and trained staff immediate access to pressurized water close to the seat of the fire — instead of hauling long hoses from distant pumps. BNBC guidance and professional design standards describe flow-rates, pipe sizes and pump requirements depending on occupancy and height. AnyFlip+1 Key functions: Rapid attack: Fighting a fire in its early stage dramatically reduces casualties and spread. Reach: Standpipes and hoses on each floor reach areas where external ladders cannot. Firefighter efficiency: Hydrants and pumps reduce setup time so FSCD crews can suppress fires faster. Property conservation: Early suppression contains damage and lowers direct economic losses. Evidence that hydrants save lives and property In multi-storey incidents, the absence of internal water supply and active firefighting (sprinklers/standpipes) has repeatedly translated into higher casualties and more severe burns as smoke and heat trap occupants. The Green Cozy Cottage case showed overcrowded floors, restaurants with unauthorized cooking and trapped people fleeing to rooftops — situations where internal hydrants + staff training could have allowed quicker containment. Al Jazeera+1 National codes (BNBC) require manual fire alarm and hydrant systems for many non-residential occupancies and give criteria for when standpipe/hydrant systems are mandatory (height, floor area, occupancy type). Where such systems are present and maintained, they form a first line of defense while FSCD arrives. BNBC sections and related fire-safety audits repeatedly recommend hydrants and dedicated fire pumps for factories and tall buildings. AnyFlip+1 Practical reasons every mall should have hydrants (concise) Immediate suppression capability — malls are high-occupancy, mixed-use spaces (shops, food courts, cinemas). Fires originating in kitchens or retail stockrooms spread fast; hydrants let trained staff and firefighters attack without delay. Al Jazeera Reduce evacuation risk — slower fire control means more people exposed to smoke and panic during evacuation; quicker knockdown lowers deaths/injuries. AP News Complement sprinklers and alarms — hydrants are not a replacement but an essential complement (sprinklers may fail or not be installed). BNBC expects fixed systems in many commercial occupancies. AnyFlip Help firefighters be effective in dense urban areas — narrow streets and traffic can delay external water supply; internal hydrants provide ready water on upper floors. Law Resource Lower economic loss and downtime — data shows huge national losses; earlier containment saves stock, infrastructure and livelihoods. The Business Standard What a good hydrant program for a mall in Bangladesh looks like Design to BNBC / professional standards — hydraulic calculations for flow rates, standpipe sizing, pump capacity and storage per BNBC (and NFPA where applicable). Ensure hydrant spacing and number match occupancy and building height. AnyFlip+1 Reliable water source + redundant pump power — municipal supply may be unreliable; include an on-site tank and diesel/electric pump with automatic switch-over. Lima Visible signage and unobstructed access — hose cabinets and external street hydrants must be clearly marked and kept clear. BNBC explicitly calls for hydrant coverage and fire apparatus access. Law Resource Periodic testing & maintenance — hoses, nozzles, valves and pumps must be tested regularly; records should be available to FSCD inspectors. dce.buet.ac.bd Staff training & drills — mall management and shop tenants must be trained to use hoses, perform initial containment and guide evacuations. Al Jazeera Coordination with FSCD — hydrant layouts, water sources and access plans shared with local fire authorities for faster, coordinated response. File Chittagong Policy & enforcement: why compliance matters now The repeated tragedies (Green Cozy Cottage 2024, FR Tower 2019, and many other building fires) are not just engineering failures — they are governance and enforcement failures. The BNBC contains provisions for hydrant and fixed firefighting arrangements for many occupancies; the gap is in enforcement, inspection and retrofitting older buildings. Stronger mandatory retrofitting rules for malls, strict inspection certificates tied to occupancy licenses, and meaningful penalties for non-compliance will save lives. Al Jazeera+1 Hydrant specification for shopping malls — recommended minimums How to use this: treat the items below as a site-specific design starting point. Final values must be determined by a qualified fire-protection engineer using hydraulic calculations, BNBC review/approval, and coordination with the local FSCD (Bangladesh Fire Service & Civil
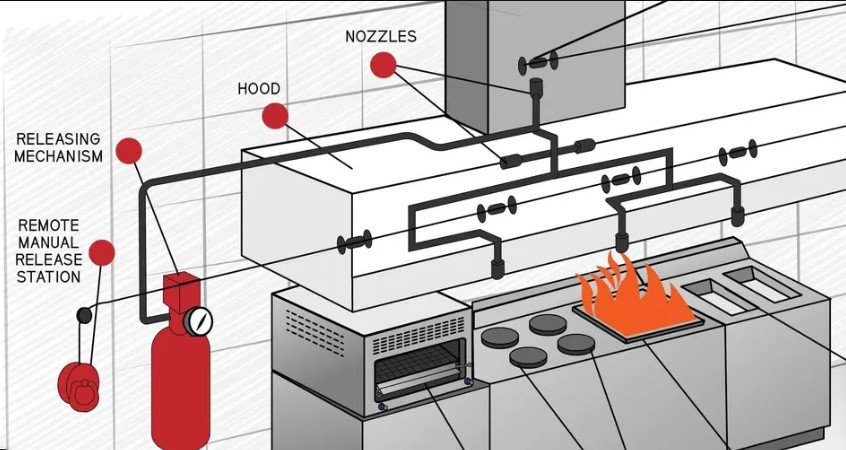
Fire Suppression System: The Safety Net Every Business Needs
When we think about fire safety, most of us imagine fire alarms ringing, sprinklers spraying water, or someone rushing with an extinguisher. But here’s the truth: by the time we react, a fire may already be out of control. That’s why industries around the world — from garment factories to data centers — rely on something more powerful, faster, and smarter: the automatic fire suppression system. 🔥 What is a Fire Suppression System? A fire suppression system is like your silent guardian. It doesn’t wait for someone to notice smoke. It doesn’t need anyone to press a button. Instead, the system is designed to detect fire instantly and activate within seconds to stop the flames before they spread. It’s not just a fire alarm — it’s a fire protection system that eliminates danger before disaster strikes. 🚨 Types of Fire Suppression Systems Not every fire is the same — and neither is every suppression system. Choosing the right fire suppression system in Bangladesh depends on your environment and risk type: Water-Based Systems – Sprinkler systems and water mist fire suppression systems. Ideal for offices, malls, and garment factories. Gas-Based Systems – Such as FM-200 fire suppression systems or CO₂ fire suppression systems. Designed for places like data centers where water would cause more damage than the fire itself. Foam Systems – Perfect for facilities dealing with flammable liquids such as fuel, oil, or chemicals. Powder & Aerosol Systems – Compact and fast-acting, ideal for industrial environments with high fire risk. Each type has a specific role in fire safety, and a fire risk assessment can determine which system is best. 🛡️ Why Fire Suppression Systems Are Essential Because fire doesn’t give warnings: Protect lives — A reliable suppression system can save workers and families from tragedy. Safeguard business assets — A single fire can destroy years of investment. Reduce downtime — Quick suppression helps operations resume faster. Ensure compliance — Meeting fire safety compliance for factories builds trust with global buyers. 🌍 Fire Safety in Bangladesh: Lessons We Cannot Ignore Bangladesh has seen devastating fire incidents — from Nimtoli to Tazreen Fashion to FR Tower. These tragedies prove how vital fire suppression systems are. Today, many garment factories in Bangladesh are investing in fire suppression installation not just to meet compliance but to protect lives, assets, and the reputation of the industry. ✅ Final Thoughts A fire suppression system is more than equipment — it’s peace of mind. It’s knowing your workplace is safe, your people are protected, and your business continuity is ensured. 👉 Fire won’t wait. Neither should we. Ensure your factory or commercial space has a proper fire suppression system in Bangladesh today. 🔎 Fire Suppression System FAQs 1. What is the difference between a fire suppression system and a sprinkler system?A sprinkler system uses water to control fires, while fire suppression systems may use water, foam, gas, or powder depending on the environment. 2. Which fire suppression system is best for factories in Bangladesh?Garment factories often use water-based sprinklers or foam systems. Sensitive areas such as data centers require FM-200 or CO₂ fire suppression systems. 3. Is a fire suppression system mandatory in Bangladesh?Yes — compliance with Bangladesh Fire Service & Civil Defence (FSCD) regulations is essential, especially for garment factories. 4. How often should a fire suppression system be maintained?Routine inspections should be done every 6 months, with professional servicing at least once a year. 5. Why should global buyers care about fire suppression systems in Bangladesh factories?Because ensuring fire safety protects workers’ lives and strengthens the supply chain reputation of buyers sourcing products from Bangladesh.
অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি: আধুনিক নিরাপত্তার সমাধান
🔥 বাংলাদেশের দ্রুত নগরায়ণ ও শিল্পায়নের যুগে, অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি একটি অপরিহার্য বিষয় হয়ে উঠেছে। পুরনো পদ্ধতিতে অগ্নি প্রতিরোধের চ্যালেঞ্জ মোকাবিলা করতে, আধুনিক প্রযুক্তি ও সমাধানগুলি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করছে। এই ব্লগে আমরা অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির বর্তমান অবস্থা, আধুনিক সিস্টেম ও সমাধানগুলি, এবং এগুলির প্রয়োগের গুরুত্ব নিয়ে আলোচনা করব। 🧯 আধুনিক অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির উদ্ভাবন ১. স্মার্ট ফায়ার ডিটেকশন সিস্টেম বর্তমানে, স্মার্ট ফায়ার ডিটেকশন সিস্টেমগুলি আগুনের প্রাথমিক সংকেত শনাক্ত করতে সক্ষম। এই সিস্টেমগুলি তাপমাত্রা, ধোঁয়া, এবং কার্বন মনোক্সাইডের মাত্রা পরিমাপ করে আগুনের উপস্থিতি সনাক্ত করে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, টেকনো অ্যাপোজি বাংলাদেশের স্মার্ট ফায়ার ডিটেকশন সিস্টেমগুলি NFPA, BNBC 2020 এবং RMG Sustainability Council এর মান অনুযায়ী ডিজাইন করা হয়েছে ২. অটোমেটেড ফায়ার সাপ্রেশন সিস্টেম অটোমেটেড ফায়ার সাপ্রেশন সিস্টেমগুলি আগুনের উপস্থিতি সনাক্ত করার সাথে সাথে স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে আগুন নিভিয়ে দেয়। এই সিস্টেমগুলি বিভিন্ন ধরনের আগুনের জন্য উপযুক্ত, যেমন পানি ভিত্তিক, ফোম ভিত্তিক, এবং গ্যাস ভিত্তিক সিস্টেম। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, টেকনো অ্যাপোজি বাংলাদেশের অটোমেটেড ফায়ার সাপ্রেশন সিস্টেমগুলি আধুনিক প্রযুক্তি ব্যবহার করে আগুন দ্রুত নিভিয়ে দেয় ৩. বিল্ডিং অটোমেশন সিস্টেম বিল্ডিং অটোমেশন সিস্টেমগুলি ফায়ার অ্যালার্ম, স্প্রিংকলার, এবং স্মোক ডিটেক্টরকে একত্রিত করে একটি সমন্বিত সিস্টেম তৈরি করে। এই সিস্টেমগুলি আগুনের উপস্থিতি সনাক্ত করার সাথে সাথে স্বয়ংক্রিয়ভাবে ব্যবস্থা গ্রহণ করে, যেমন স্প্রিংকলার চালু করা এবং কর্তৃপক্ষকে সতর্ক করা। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, রিলায়েন্ট-ইস্ট বাংলাদেশের বিল্ডিং অটোমেশন সিস্টেমগুলি আগুনের উপস্থিতি দ্রুত সনাক্ত করে এবং ব্যবস্থা গ্রহণ করে 🏢 বাংলাদেশে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির প্রয়োগ বাংলাদেশে বিভিন্ন শিল্প ও প্রতিষ্ঠানগুলিতে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির প্রয়োগ বৃদ্ধি পাচ্ছে। রেডি-মেড গার্মেন্ট (RMG) সেক্টরে, অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির প্রয়োগ নিশ্চিত করতে আন্তর্জাতিক সংস্থাগুলি কাজ করছে। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, আন্তর্জাতিক শ্রম সংস্থা (ILO) এবং মার্কিন যুক্তরাষ্ট্রের শ্রম দপ্তরের অর্থায়নে “Improving Fire and General Building Safety in Bangladesh” প্রকল্পটি RMG সেক্টরে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা উন্নত করতে কাজ করছে 📜 বাংলাদেশে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা বিধিমালা বাংলাদেশে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা বিধিমালা বাস্তবায়নের জন্য বাংলাদেশ ন্যাশনাল বিল্ডিং কোড (BNBC) ২০২০ গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করছে। এই কোডে অগ্নি প্রতিরোধের জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় শর্তাবলী, প্রস্থান পথের ব্যবস্থা, এবং আগুন, ধোঁয়া ও বিষাক্ত গ্যাস থেকে জীবন রক্ষার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় ব্যবস্থা উল্লেখ করা হয়েছে ❓ অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি সম্পর্কিত সাধারণ প্রশ্নাবলী প্রশ্ন ১: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি কী? উত্তর: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি এমন একটি সিস্টেম যা আগুনের উপস্থিতি সনাক্ত করে এবং তা নিয়ন্ত্রণ বা নিভিয়ে দেয়, যাতে মানুষের জীবন ও সম্পত্তি রক্ষা করা যায়। প্রশ্ন ২: আধুনিক অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির উদাহরণ কী কী? উত্তর: আধুনিক অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির উদাহরণ হিসেবে স্মার্ট ফায়ার ডিটেকশন সিস্টেম, অটোমেটেড ফায়ার সাপ্রেশন সিস্টেম, এবং বিল্ডিং অটোমেশন সিস্টেম উল্লেখযোগ্য। প্রশ্ন ৩: বাংলাদেশে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির প্রয়োগ কোথায় দেখা যায়? উত্তর: বাংলাদেশে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির প্রয়োগ রেডি-মেড গার্মেন্ট (RMG) সেক্টর, হাসপাতাল, শিক্ষা প্রতিষ্ঠান, এবং বাণিজ্যিক ভবনগুলিতে দেখা যায়। প্রশ্ন ৪: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা বিধিমালা বাস্তবায়নের জন্য কোন কোড অনুসরণ করা হয়? উত্তর: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা বিধিমালা বাস্তবায়নের জন্য বাংলাদেশ ন্যাশনাল বিল্ডিং কোড (BNBC) ২০২০ অনুসরণ করা হয়। প্রশ্ন ৫: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি ব্যবহারের সুবিধা কী কী? উত্তর: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি ব্যবহারের মাধ্যমে আগুনের প্রাথমিক পর্যায়ে সনাক্তকরণ, দ্রুত প্রতিক্রিয়া, এবং মানুষের জীবন ও সম্পত্তি রক্ষা সম্ভব হয়। ✅ উপসংহার অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি আধুনিক ভবন, শিল্প প্রতিষ্ঠান, এবং অন্যান্য স্থাপনার জন্য অপরিহার্য। এটি মানুষের জীবন ও সম্পত্তি রক্ষায় গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ভূমিকা পালন করে। বাংলাদেশে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তির প্রয়োগ বৃদ্ধি পাচ্ছে এবং এটি ভবিষ্যতে আরও উন্নত হবে। 📞যোগাযোগ আপনার প্রতিষ্ঠানে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রযুক্তি ও সর্বোত্তম পরামর্শ ও সেবা নিতে চাইলে এখানে যোগাযোগ করতে পারেন । 01404-022297 | 01711-195266 nazrul@safetysource.com.bd 67/A (3rd Floor), Aziz Square, Rabindra Sarani, Sector: 07, Uttara, Dhaka-1230 www.safetysource.com.bd
ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান ও সনদ রিনিউ করুন – নিরাপত্তাই আপনার প্রথম অগ্রাধিকার
একটি ছোট্ট অসাবধানতাই মুহূর্তের মধ্যে ভয়াবহ অগ্নিকাণ্ডের কারণ হতে পারে। আর এই ভয়াবহতার সামনে সবার আগে যে জিনিস আপনাকে, আপনার পরিবারকে বা কর্মীদের বাঁচাতে সাহায্য করতে পারে, সেটি হলো ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান এবং এর কার্যকারিতা নিশ্চিত করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় সনদ (Certificate of Effectiveness)। কেন ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান জরুরি? প্রথমিক সুরক্ষা: আগুন লাগলে কীভাবে বের হতে হবে, কোন এক্সিট ব্যবহার করতে হবে, কোথায় অগ্নিনির্বাপক যন্ত্র রাখা আছে—এসব বিষয় ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যানে পরিষ্কারভাবে উল্লেখ থাকে। প্রস্তুতি নিশ্চিতকরণ: কর্মী বা বাসিন্দারা জরুরি পরিস্থিতিতে আতঙ্কিত না হয়ে সঠিক পদক্ষেপ নিতে পারে। আইনগত প্রয়োজনীয়তা: নতুন বা পুরাতন বিল্ডিং, শিল্প প্রতিষ্ঠান, কারখানা—সব জায়গায় ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান ও সনদ নেওয়া আইনগত বাধ্যবাধকতা। সম্পদ রক্ষা: প্রাণহানি প্রতিরোধের পাশাপাশি এটি আপনার সম্পদ ও বিনিয়োগকেও সুরক্ষা দেয়। কার্যকারিতা সনদ (Validity Certificate) কেন নবায়ন করবেন? সময়ের সাথে যন্ত্রপাতি (ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার, হোস পাইপ, ডিটেক্টর ইত্যাদি) কার্যকারিতা হারাতে পারে। নিয়মিত চেক না করলে জরুরি অবস্থায় এগুলো কাজ না-ও করতে পারে। সনদ রিনিউ করলে প্রমাণিত হয় যে আপনার স্থাপনায় সব সেফটি যন্ত্রপাতি কার্যকর এবং সঠিকভাবে রক্ষণাবেক্ষিত। এটি অনেক সময় ইনস্যুরেন্স দাবি করার জন্যও অপরিহার্য। 🛠️ কীভাবে রিনিউ করবেন? ফায়ার সেফটি পরিদর্শন: অনুমোদিত সংস্থা বা কর্তৃপক্ষ আপনার বিল্ডিং/প্রতিষ্ঠানের সব সেফটি সিস্টেম পরীক্ষা করবে। রক্ষণাবেক্ষণ ও মেরামত: যদি কোথাও ত্রুটি পাওয়া যায়, তা ঠিক করার ব্যবস্থা করতে হবে। সনদ প্রদান: সব ঠিক থাকলে কার্যকারিতা সনদ প্রদান করা হবে এবং নির্দিষ্ট সময় পর্যন্ত এটি বৈধ থাকবে। 📌 কাদের জন্য জরুরি? আবাসিক ভবন (নতুন ও পুরাতন) অফিস ও বাণিজ্যিক ভবন শিল্প প্রতিষ্ঠান ও কারখানা শিক্ষাপ্রতিষ্ঠান, হাসপাতাল, শপিং মল ইত্যাদি 🔑 উপসংহার ফায়ার সেফটি শুধু আইন মেনে চলার বিষয় নয়—এটি আপনার জীবন, কর্মীদের নিরাপত্তা এবং সম্পদ সুরক্ষার সাথে সরাসরি সম্পর্কিত। তাই দেরি না করে আজই আপনার ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান তৈরি ও সনদ রিনিউ করুন। মনে রাখবেন— 👉 “অল্প অবহেলা বড় বিপর্যয় ডেকে আনতে পারে। নিরাপত্তাই হোক আপনার প্রথম অগ্রাধিকার।” আপনার নতুন, পুরাতন বিল্ডিং, প্রতিষ্ঠান অথবা কারখানার জন্য ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান ও কার্যকারিতার সনদ এর জন্য যোগাযোগ করুন। 👉 সেফটি সোর্স লিমিটেড www.safetysource.com.bd , ফায়ার সার্ভিস এন্ড সিভিল ডিফেন্স এবং কলকারখানা অধিদপ্তর-এর সকল ক্যাটাগরিতে নিবন্ধিত। বিস্তারিত জানতে কল করুনঃ 📱 01404-022297 📱 01711-195266 ❓ সাধারণ কিছু প্রশ্নোত্তর (FAQ) 1. ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান কী? ফায়ার সেফটি প্ল্যান হলো একটি পরিকল্পনা যেখানে জরুরি অবস্থায় (আগুন লাগলে) কিভাবে বের হতে হবে, কোথায় অগ্নিনির্বাপক যন্ত্র রাখা আছে, এক্সিট রুট কোথায়—এসব বিস্তারিত উল্লেখ থাকে। 2. ফায়ার সেফটি সনদ (Certificate of Effectiveness) কেন প্রয়োজন? এটি প্রমাণ করে যে আপনার বিল্ডিং বা প্রতিষ্ঠান ফায়ার সেফটি মানদণ্ড পূরণ করেছে এবং ব্যবহৃত যন্ত্রপাতি কার্যকর অবস্থায় আছে। 3. কতদিন পর পর ফায়ার সেফটি সনদ রিনিউ করতে হয়? সাধারণত প্রতি বছর অথবা কর্তৃপক্ষ নির্ধারিত সময় অন্তর সনদ নবায়ন করতে হয়। নিয়মিত রিনিউ করলে যন্ত্রপাতির কার্যকারিতা বজায় থাকে। 4. কারা এই সনদ নিতে বাধ্য? নতুন ও পুরাতন সব ধরনের বিল্ডিং, অফিস, কারখানা, শিল্প প্রতিষ্ঠান, শিক্ষাপ্রতিষ্ঠান, হাসপাতাল, শপিং মলসহ সব স্থাপনাতেই এটি আইনত বাধ্যতামূলক। 5. কোথায় যোগাযোগ করলে সনদ রিনিউ করা যাবে? আপনি সেফটি সোর্স লিমিটেড-এর সাথে যোগাযোগ করতে পারেন। তারা ফায়ার সার্ভিস এন্ড সিভিল ডিফেন্স ও কলকারখানা অধিদপ্তরের সকল ক্যাটাগরিতে নিবন্ধিত প্রতিষ্ঠান। 📞 যোগাযোগ করুন 📱 01404-022297 | 01711-195266📧 nazrul@safetysource.com.bd🏢 67/A (3rd Floor), Aziz Square, Rabindra Sarani, Sector: 07, Uttara, Dhaka-1230🌐 www.safetysource.com.bd
অগ্নিকাণ্ড প্রতিরোধ ও ঘরের অগ্নি সুরক্ষা: সর্বশেষ তথ্যভিত্তিক গাইড
অগ্নিকাণ্ড প্রতিরোধ ও ঘরের অগ্নি সুরক্ষা: সর্বশেষ তথ্যভিত্তিক গাইড অগ্নিকাণ্ড প্রতিরোধের গুরুত্ব বাংলাদেশে প্রতিদিন গড়ে প্রায় ৭৩টি অগ্নিকাণ্ড ঘটে। জীবন ও সম্পদ রক্ষা করতে সচেতনতা এবং নিরাপত্তা ব্যবস্থা অপরিহার্য। ছোট পদক্ষেপ যেমন সঠিক অগ্নিনির্বাপন যন্ত্র স্থাপন, নিয়মিত চেকআপ, এবং পরিবারের সদস্যদের সচেতনতা জীবন রক্ষা করতে পারে। বাংলাদেশে অগ্নিকাণ্ডের পরিসংখ্যান (২০২৪) মোট অগ্নিকাণ্ড: ২৬,৬৫৯টি মৃত্যু: ১৪০ জন আহত: ৩৪১ জন গড়ে প্রতিদিন: ৭৩টি অগ্নিকাণ্ড প্রধান কারণ: বৈদ্যুতিক শর্ট সার্কিট (~৩৪%), সিগারেট/বিড়ি অবশিষ্টাংশ (~১৫.৫%), রান্না/চুলা দুর্ঘটনা (~১১.৫%), গ্যাস লিক ও পাইপলাইন সমস্যা সর্বাধিক অগ্নিকাণ্ড: বাসাবাড়ি (৭,১৩১টি, মোট ঘটনার ২৬.৭৪%) আর্থিক ক্ষতি: প্রায় ৪৪৭ কোটি টাকা; উদ্ধারকৃত সম্পদের মূল্য: ১,৯৭৪ কোটি টাকা পরিসংখ্যান প্রমাণ করে, অগ্নি সুরক্ষা এখন বিলাসিতা নয়, এটি অপরিহার্য। বাড়ির জন্য সেরা অগ্নিনির্বাপন ব্যবস্থা আগুনের ধরন যন্ত্রের ধরন ব্যবহারের স্থান ক্লাস A (কাঠ, কাপড়, কাগজ) পানি, ফোম, ABC ড্রাই পাউডার বসার ঘর, শোবার ঘর ক্লাস B (তেল, তরল জ্বালানি) ফোম বা ড্রাই পাউডার রান্নাঘর, গ্যারেজ ক্লাস C (বৈদ্যুতিক আগুন) CO₂ বা ড্রাই পাউডার বৈদ্যুতিক যন্ত্রপাতি থাকা কক্ষ ক্লাস F (রান্নার তেল, গ্রিজ) ওয়েট কেমিক্যাল এক্সটিংগুইশার রান্নাঘর পণ্য বাছাইয়ের টিপস: • FSCD অনুমোদিত ব্র্যান্ড কিনুন। • প্রেসার গেজ, মেয়াদ এবং ব্যবহারযোগ্যতা পরীক্ষা করুন। • পরিবারের আকার ও ঝুঁকি অনুযায়ী সঠিক ক্ষমতা বেছে নিন। ঘরের অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা টিপস রান্নার পরে গ্যাস সিলিন্ডার এবং চুলা বন্ধ রাখুন। বৈদ্যুতিক লাইন ও সকেট অতিরিক্ত লোডে ব্যবহার করবেন না। ধোঁয়া শনাক্তকারী (Smoke Detector) স্থাপন করুন এবং নিয়মিত পরীক্ষা করুন। অগ্নিনির্বাপন যন্ত্র সহজে পাওয়া যায় এমন স্থানে রাখুন। ফায়ার ব্ল্যাঙ্কেট এবং বালতি পানি প্রস্তুত রাখুন। জরুরি বহির্গমন পথ পরিষ্কার রাখুন। ঘরে স্মোক অ্যালার্ম (ধোঁয়া-সংকেত) ও ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার স্থাপন করুন এবং নিয়মিত পরীক্ষা করুন। বিদ্যুৎ সংযোগ, গ্যাসের চুলা ও দাহ্যবস্তু যেমন দিয়াশলাই, জ্বালানি, শুকনো পাতা থেকে সাবধান থাকুন। আগুন লাগলে দ্রুত বাইরে বের হওয়ার জন্য আগে থেকে একটি পরিকল্পনা তৈরি করুন। জরুরি প্রয়োজনে বাড়ির বাইরে বের হওয়ার জন্য অন্তত দুটি পথ ঠিক রাখুন, যেখানে একটি জানালা বা বিকল্প পথ থাকতে পারে। রান্নাঘরে তেল বা গ্রিজের আগুনের জন্য ওয়েট কেমিক্যাল এক্সটিংগুইশার ব্যবহার করুন। শিশুদের আগুনের কাছ থেকে দূরে রাখুন এবং আগুন সম্পর্কিত সচেতনতা শিখান। বৈদ্যুতিক যন্ত্রপাতি ব্যবহার না হলে প্লাগ খুলে রাখুন। ধোঁয়া শনাক্তকারী ও অ্যালার্মের ব্যাটারি প্রতি ছয় মাসে একবার পরিবর্তন করুন। মাসে একবার ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশারের প্রেসার গেজ পরীক্ষা করুন। পরিবারের সবাইকে ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার ব্যবহারের পদ্ধতি (PASS: Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep) শেখান। এই টিপসগুলো মেনে চললে আপনার ঘর এবং পরিবারের নিরাপত্তা উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে বৃদ্ধি পাবে। ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার কোথায় পাওয়া যাবে • অনুমোদিত ফায়ার সেফটি শোরুম থেকে। • অনলাইন ই-কমার্স সাইট (দারাজ, আজকেরডিল)। • FSCD অনুমোদিত সরবরাহকারীর কাছ থেকে। • দাম: ১,৫০০ থেকে ১০,০০০ টাকা, সাইজ ও ধরন অনুযায়ী। অগ্নিনির্বাপন যন্ত্রপাতি কিনতে ও দ্রুত রেসপন্স পেতে নিচের নাম্বার গুলিতে যোগাযোগ করতে পারেন 🌐 ওয়েবসাইট: Safety Source Limited 📱 মোবাইল: +8801914-508497, +8801711-195266 📧 ইমেইল: info@safetysource.com.bd বড় অগ্নিকাণ্ড উদাহরণ • ঢাকার বেইলি রোড ফায়ার (২৯ ফেব্রুয়ারি ২০২৪): ৪৬ জন নিহত। • মূল সমস্যা: গ্যাস সিলিন্ডার সংরক্ষণ, জরুরি বহির্গমন পথের অভাব। • শিক্ষা: ভবনের ডিজাইন ও ফায়ার সেফটি মানদণ্ড মেনে নির্মাণ অত্যাবশ্যক। কেন অগ্নিকাণ্ড বেড়ে চলেছে? • ঘনবসতিপূর্ণ শহরে নিরাপত্তা মানদণ্ড না মানা। • বৈদ্যুতিক তারের ত্রুটি ও অবৈধ সংযোগ। • গ্যাস লাইনের নিয়মিত রক্ষণাবেক্ষণের অভাব। • সাধারণ মানুষের অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা সচেতনতার অভাব। এটি জীবন ও সম্পদ রক্ষার অপরিহার্য অংশ। প্রতিদিনের ছোটো সতর্কতা যেমন সঠিক অগ্নিনির্বাপন যন্ত্র স্থাপন, ধোঁয়া শনাক্তকারী ব্যবহার, এবং পরিবারের সকলের সচেতনতা বড় দুর্ঘটনা থেকে রক্ষা করতে পারে। বাংলাদেশে বাড়ির অগ্নিকাণ্ডের হার উদ্বেগজনক হলেও, সঠিক পরিকল্পনা ও নিয়মিত চেকআপের মাধ্যমে ঝুঁকি উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে কমানো সম্ভব। আগুন লাগার আগে প্রস্তুতি, জরুরি বের হওয়ার পথ নির্ধারণ, এবং নিয়মিত অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা ড্রিল আপনাকে এবং আপনার পরিবারের সদস্যদের সুরক্ষা দিতে পারে। সর্বোপরি, সচেতনতা এবং প্রস্তুতি হলো অগ্নিকাণ্ড প্রতিরোধের সবচেয়ে শক্তিশালী হাতিয়ার। আপনার ঘরকে নিরাপদ এবং আগুনমুক্ত রাখতে আজই এই পদক্ষেপগুলো গ্রহণ করুন। নিরাপদ জীবন আপনার হাতেই। FAQs (প্রায়শই জিজ্ঞাসিত প্রশ্ন) Q1: ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার কিভাবে ব্যবহার করবো? A: PASS পদ্ধতি অনুসরণ করুন: Pull pin, Aim nozzle, Squeeze lever, Sweep across base of fire। Q2: কোন ধরণের ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার রান্নাঘরের জন্য ভালো? A: ওয়েট কেমিক্যাল এক্সটিংগুইশার তেল ও গ্রিজের আগুন নিয়ন্ত্রণে কার্যকর। Q3: অগ্নিনির্বাপন যন্ত্রের মেয়াদ কত? A: সাধারণত ৫ বছর, তবে নিয়মিত চেকআপ ও রিফিলের পর মেয়াদ বৃদ্ধি সম্ভব। Q4: বাংলাদেশে অনুমোদিত ফায়ার এক্সটিংগুইশার কোথায় পাওয়া যায়? A: FSCD অনুমোদিত শোরুম ও অনলাইন মার্কেটপ্লেস থেকে। এখানে পাবেন: Safety Source Limited 📱 মোবাইল: +8801914-508497অগ্নিকাণ্ড প্রতিরোধ বাংলাদেশ, +8801711-195266
অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থা কেন জরুরি: 10 গুরুত্বপূর্ণ কারণ যা আপনার প্রতিষ্ঠানকে রক্ষা করবে
আজকের আধুনিক দফতর, কারখানা, হাসপাতাল এবং বিভিন্ন প্রতিষ্ঠানে অগ্নি ঝুঁকি একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ বিষয় হয়ে দাঁড়িয়েছে। অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থা শুধুমাত্র একটি আইনগত বাধ্যবাধকতা নয়, বরং এটি আপনার প্রতিষ্ঠানের নিরাপত্তা, কর্মচারীর জীবন এবং অর্থনৈতিক ক্ষতি কমানোর একটি অপরিহার্য উপাদান। এই আর্টিকেলটি আপনাকে জানাবে কেন অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থা অত্যন্ত জরুরি এবং কীভাবে এটি কার্যকরভাবে প্রয়োগ করা যায়। আধুনিক কর্মক্ষেত্রে অগ্নির ঝুঁকি বোঝা বৈদ্যুতিক অগ্নি ঝুঁকি বৈদ্যুতিক সংযোগের ভুল, পুরোনো তার এবং ওভারলোডিং প্রায়ই অগ্নির প্রধান কারণ। নিয়মিত রক্ষণাবেক্ষণ এবং সার্টিফায়েড ইলেকট্রিশিয়ান ব্যবহার করা অত্যন্ত জরুরি। রাসায়নিক অগ্নি ঝুঁকি কারখানা ও গবেষণা কেন্দ্রগুলোতে রাসায়নিক পদার্থের অনিয়মিত সংরক্ষণ অগ্নির সম্ভাবনা বাড়ায়। নিরাপদ সংরক্ষণ, লেবেলিং এবং প্রশিক্ষণ কর্মসূচি গ্রহণ অপরিহার্য। কার্যকর অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থার মূল উপাদান অগ্নি এলার্ম এবং সনাক্তকরণ ব্যবস্থা স্বয়ংক্রিয় অ্যালার্ম সিস্টেম ধোঁয়া ও তাপ শনাক্তকরণ সেন্সর জরুরি সিগন্যাল এবং সতর্কতা স্প্রিংকলার সিস্টেম স্বয়ংক্রিয় suppression বিভিন্ন ধরণের coverage এবং maintenance নির্দেশিকা দ্রুত প্রতিক্রিয়া প্রদান পোর্টেবল অগ্নিনির্বাপক যন্ত্র বিভিন্ন প্রকার (পানি, ফোম, CO2, ড্রাই কেমিক্যাল) যথাযথ স্থাপন ও ব্যবহার নির্দেশিকা আইনগত এবং নিয়ন্ত্রক বাধ্যবাধকতা শ্রমিক নিরাপত্তা মান দেশীয় আইন ও আন্তর্জাতিক নীতিমালা অনুযায়ী প্রতিষ্ঠানগুলিকে অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা ব্যবস্থা স্থাপন বাধ্যতামূলক। বীমা সুবিধা এবং আইনি সুরক্ষা সঠিক অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা ব্যবস্থা থাকলে বীমা ক্লেইম দ্রুত এবং সহজ হয়, এবং আইনি ঝুঁকি কমে। অগ্নি দুর্ঘটনার আর্থিক প্রভাব সরাসরি ও অপ্রত্যক্ষ খরচ সরাসরি: সম্পত্তি ক্ষতি, পুনর্নির্মাণ খরচ অপ্রত্যক্ষ: ব্যবসার ক্ষতি, ব্র্যান্ড ইমেজ ক্ষতি বাস্তব জীবন উদাহরণ বিশ্বের বিভিন্ন কারখানা ও অফিসে অগ্নি দুর্ঘটনার উদাহরণ থেকে শেখা যায় যে সঠিক প্রস্তুতি ও সিস্টেম থাকলে ক্ষতি অনেক কমানো সম্ভব। অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রশিক্ষণ ও সচেতনতা ফায়ার রেসপন্স প্ল্যান তৈরি নিরাপদ পদক্ষেপ ও দায়িত্ব জরুরি নির্গমনের রুট কর্মচারীদের প্রশিক্ষণ নিয়মিত ফায়ার ড্রিল মাসিক বা ত্রৈমাসিক ফায়ার ড্রিল কার্যকারিতা নিরীক্ষণ এবং রিপোর্টিং প্রযুক্তিগত অগ্রগতি স্মার্ট সিস্টেম: IoT এবং AI ভিত্তিক সনাক্তকরণ রিয়েল-টাইম মনিটরিং স্বয়ংক্রিয় suppression এবং alerts অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা সম্পর্কিত সাধারণ ভুল ধারণা “আমাদের প্রতিষ্ঠানে আগুন লাগবে না” “পুরোনো বিল্ডিংতে নিরাপত্তা সিস্টেম লাগানো অর্থের অপচয়” প্রকৃতপক্ষে, অগ্নি দুর্ঘটনা যেকোনো সময় ঘটতে পারে এবং এটি প্রতিরোধযোগ্য। পরিবেশগত দিক পরিবেশবান্ধব অগ্নিনির্বাপক এজেন্ট পুনঃব্যবহারযোগ্য ও কম ক্ষতিকর পদার্থ টেকসই নিরাপত্তা ব্যবস্থা দৈনন্দিন পরিচালনায় অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা সংযোজন নিয়মিত রক্ষণাবেক্ষণ ও অডিট দায়িত্ব ভাগাভাগি এবং কর্মচারী সচেতনতা ঝুঁকি মূল্যায়ন ও আপডেট করা নিরাপত্তা নীতি FAQs About Fire Suppression Systems Q1: অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থা কত প্রকারের হয়?A: প্রধানত তিন প্রকার: অগ্নি এলার্ম ও ডিটেকশন, স্প্রিংকলার সিস্টেম, এবং পোর্টেবল অগ্নিনির্বাপক যন্ত্র। Q2: স্প্রিংকলার সিস্টেম কি শুধুমাত্র বড় অফিসের জন্য প্রয়োজন?A: নয়, ছোট ব্যবসা, বাড়ি ও হাসপাতালেও স্প্রিংকলার সিস্টেম কার্যকর। Q3: নিয়মিত ফায়ার ড্রিল কতবার করা উচিত?A: মাসিক বা ত্রৈমাসিক ভিত্তিতে, কর্মচারীর সংখ্যা ও কার্যক্রমের উপর নির্ভর করে। Q4: অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা প্রশিক্ষণ কি বাধ্যতামূলক?A: হ্যাঁ, বিশেষত বড় প্রতিষ্ঠান ও কারখানার জন্য। Q5: কোন ধরণের অগ্নিনির্বাপক যন্ত্র সবচেয়ে কার্যকর?A: অবস্থান ও ঝুঁকির ধরণের উপর নির্ভর করে। সাধারণত CO2, ফোম ও ড্রাই কেমিক্যাল সর্বাধিক ব্যবহৃত। Q6: প্রযুক্তিগত অগ্রগতি কিভাবে অগ্নি সুরক্ষা উন্নত করছে?A: AI এবং IoT-ভিত্তিক সনাক্তকরণ দ্রুত সতর্কতা প্রদান করে, ক্ষয়ক্ষতি কমায়। আপনার প্রতিষ্ঠান, অফিস বা কারখানায় সম্পূর্ণ অগ্নি নিরাপত্তা নিশ্চিত করতে যোগাযোগ করতে পারেন-Safety Source limited এর সাথে । তারা সকল ধরনের অগ্নিনির্বাপণ যন্ত্র, সরঞ্জাম সরবরাহ, ইনস্টলেশন এবং রক্ষণাবেক্ষণ পরিষেবা প্রদান করে । https://www.safetysource.com.bd/product/ মোবাইল: +8801914-508497, +8801711-195266ইমেইল: info@safetysource.com.bd অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থা শুধু একটি বাধ্যবাধকতা নয়, এটি প্রতিষ্ঠান, কর্মচারী এবং সম্পদের নিরাপত্তা নিশ্চিত করার একটি অপরিহার্য উপায়। সঠিক প্রস্তুতি, প্রযুক্তির ব্যবহার এবং নিয়মিত প্রশিক্ষণ প্রতিষ্ঠানে অগ্নি ঝুঁকি উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে কমায়। আজই আপনার প্রতিষ্ঠানে অগ্নিনির্বাপণ ব্যবস্থা আপডেট করুন এবং নিরাপদ ভবিষ্যৎ নিশ্চিত করুন।